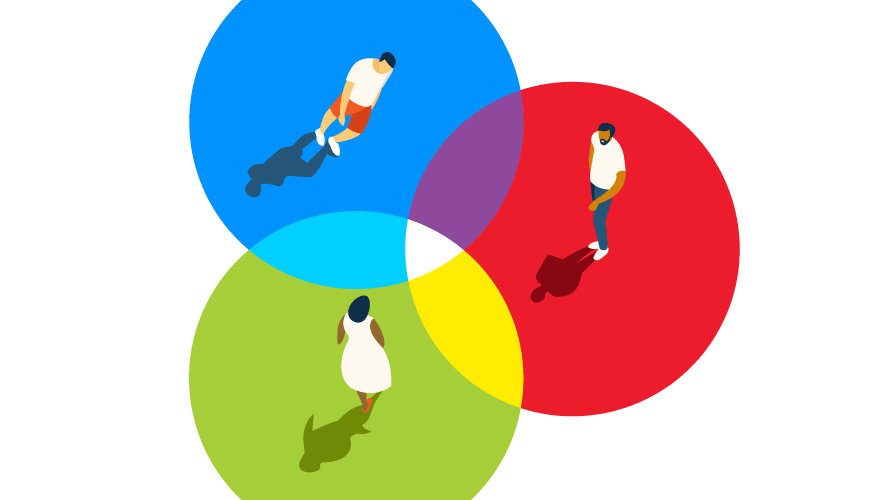
Meet the 3 Key Roles Within ESRM
Enterprise security risk management (ESRM) shifts security professionals from managing a security function to being a trusted advisor and partner for asset owners, taking a holistic view or risk rather than addressing standalone threats.
To understand the approach, you first need to get acquainted with the three critical roles within ESRM.

Asset Owner
The asset owner is the person most directly responsible for the successful operation of an asset.
ESRM assigns this person responsibility for the risk to a particular asset because the asset owner understands this territory best. This empowers them to make decisions about risks to their assets.
In an ESRM approach, the asset owner is the risk owner.

Security Professional
With an ESRM approach, security professionals act as security risk subject matter experts and trusted advisors to asset owners, executive management, and other stakeholders.
The security professional guides the asset owner through the security risk decision making process and can lead agreed-upon mitigation actions.
Executive Management
This person belongs to the highest level of executive leadership in an organization, like the C-suite or an executive committee.
In some organizations, asset owners may also be executive managers, but top management is above the security function’s leader, such as the CSO.
For ESRM to be successful, security professionals must identify, engage, and align with stakeholders and asset owners throughout the organization. This enables the development of more positive, valuable partnerships and a greater sense of ownership and buy-in across the organization.
To learn more about ESRM, consider pursuing the ASIS International Essentials of ESRM certificate program, which provides a broad overview of the ESRM approach and how to apply it in your organization. You can also assess your ESRM progress with this free ESRM maturity self-assessment.